In
eukaryotic cells, DNA wraps around a histone octamer consisting of two
copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. N terminal of each
histone can be modified and have different functions. There are
different types of modifications. The types of modification and the
exact position at which the modifications occur can influence several
DNA-based transactions including, but not limited to the regulation of
gene expression, DNA replication, and DNA damage repair. Methylation
is one type of histone modification. The major family of enzymes that
can methylate lysine on histones are called the SET domain histone
lysine methyltransferases (HKMTs).
SET
domain was initially characterized in the Drosophila proteins Suppressor
of variegation 3-9 [Su(var)3-9], Enhancer of zeste [E(z)], and Trithorax
(Trx), hence the name.
SET domain proteins transfer he S- adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet) methyl group to the ℇ-amine of a lysine residue on histone or nonhistone proteins, leaving a methylated lysine residue and the cofactor by-product S- adenosyl-L-homocysteine(AdoHcy)
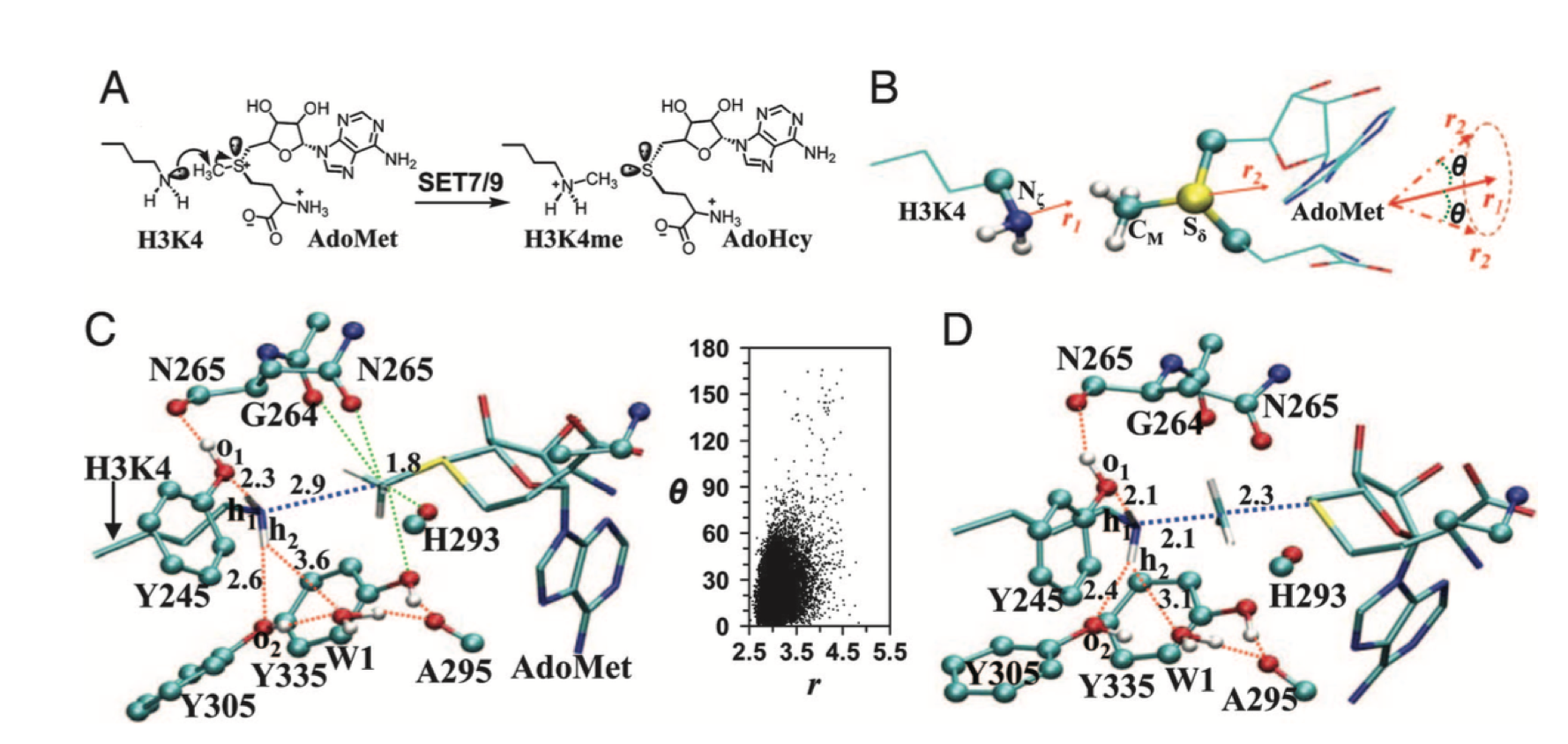
|